The Record in Stereo option controls whether new recordings are created in mono or stereo. Changing this option will not affect the currently open file - it only applies when a new file is subsequently created. You will not be able to make any changes to this option if recording is in progress.
This option does not appear if the sound card does not allow any inputs.
Record in Stereo has an effect on file usage. If you choose mono, you will save file space, but you may have difficulty transferring the saved audio data to programs other than Intonia.
Sample Rate for Recording controls how many samples per second are measured when recording. Changing this option will not affect the currently open file - it only applies when a new file is subsequently created. You will not be able to make any changes to this option if recording is in progress.
The range of acceptable values depends on the sound card. This option does not appear if the sound card does not allow any inputs.
Since this option only applies to newly created files, if you read a .WAV file from disk you cannot use this option to determine the sample rate of the file. Instead, use the Properties command on the File Menu to list the properties of the currently-open file.
Sample Rate for Recording has an effect on both file usage and processor usage. The default value is 44,100, which is the standard for audio CDs. Change it to a lower value if you want to save file space, or to a higher value if you want higher frequency response. The range of permissible values depends on your sound card. If you choose a sample rate other than 44,100, you may have difficulty transferring the saved audio data to programs other than Intonia.
If you use the "What You Hear" option of your sound card to analyze music from a digital source such as YouTube or an MP3 player, you must set Sample Rate for Recording to match the rate of the source. YouTube uses a sample rate of 22,100 kHz. MP3 files have various rates: use a tool such as Audacity to find out the sample rate of each file.
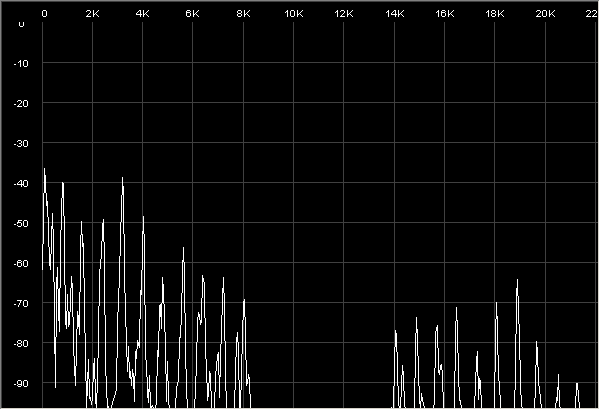
A symptom of of an incorrectly set Sample Rate when recording from digital sourses is aliasing. The screenshot below shows the Spectrum View of a violin note from a 22.05 KHz source recorded by Intonia at 44.1 KHz. The spectrum shows a V shape, approximately symmetrical around the midpoint. The peaks above 11 KHz are the product of aliasing. They mirror the peaks below, and only confuse the pitch-detection algorithm.

The Analyze Stereo Channel option applies when there is stereo data. You have a choice or analyzing the right channel, the left channel, or the two channels combined.
When One-Touch Play/Record is checked, clicking File - New will automatically select the Record and Pause buttons, and clicking File - Open will automatically select the Play and Pause buttons. Reaching the end of the tape on playback will select the Pause button.
If you don't want this behavior, uncheck One-Touch Play/Record. Reaching the end of tape on playback will unselect the Play button.
If Allow Overwrite is unchecked, you may not record over material you previously recorded or read from a file. If you click the record button, the needle will be first placed at the end of the file. Check this option if you want to be able to overwrite.
There is no undo capability in this program, so use Allow Overwrite with caution.
Paste and overwrite controls how pasting works after a cut or a copy. If this box is checked, the pasted sound will overwrite any pre-existing sound at the same points in time, analogous to re-recording the same length of tape. If this box is unchecked, the pasted sound will be inserted, analogous to splicing a section of tape into the middle. (If you paste at the end of the file, the setting of this box is immaterial.)
There is no undo capability in this program, so use Paste and Overwrite with caution.
The Max Audio File Length option controls how much sound the computer will store. Set this number to a low value if you don't care about saving anything and want to conserve system resources, set it to a high number if you're interested in analyzing or saving longer recordings. A normal CD contains up to about 74 minutes of music, but saving this much sound will require about 750 megabytes of disk space on your computer.
The maximum value you can set this option to corresponds to 2 gigabytes on the disk. For stereo recording at the standard rate of 44,100 samples per second, this works out to about 3 hours and 22 minutes. Recording in monaural doubles this limit.
When the amount of recorded sound exceeds the Max Audio File Length, sound at the beginning of the file will be removed to make room for the new sound. This is analogous to splicing tape into a loop. If you want, you can set Max Audio File Length to a small number of minutes, start the program recording, and leave it running forever without any penalty.